Page 10 - reflections_newsletter10
P. 10
REFLECTIONS
Dyslipidaemia
Dyslipidaemia Global Newsletter #10 2025
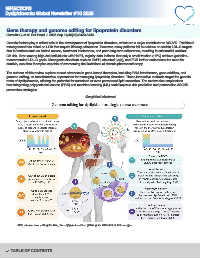
Gene therapy and genome editing for lipoprotein disorders. Dyslipidaemia
Gurevitz C, et al. Eur Heart J. 2025 Sep 14;46(35):3420-3433.
Genetic factors play a critical role in the development of lipoprotein disorders, which are a major contributor to ASCVD. Traditional
management has relied on LLTs that require lifelong adherence. However, many patients fail to achieve or sustain LDL-C targets
due to barriers such as limited access, treatment intolerance, and poor long-term adherence, resulting in substantial residual
CV risk. Even among high-risk individuals with HeFH, registry data indicate that only a small fraction (~2%) achieve guideline-
recommended LDL-C goals. Monogenic disorders such as HoFH, elevated Lp(a), and FCS further underscore the need for
durable, one-time therapies capable of overcoming the limitations of chronic pharmacotherapy.
The authors of this review explore recent advances in gene-based therapies, including RNA interference, gene addition, and
genome editing, as transformative approaches for managing lipoprotein disorders. These innovative methods target the genetic
roots of dyslipidaemia, offering the potential for sustained or even permanent lipid correction. The review also emphasises
how integrating polygenic risk scores (PRS) and machine learning (ML) could improve risk prediction and personalise ASCVD
prevention strategies.
Graphical abstract
ABE, adenine base editing; GaINAc, N-acetylgalactosamine; gRNA, guide RNA; LDLR, LDL receptor.
TABLE OF CONTENTS