Page 6 - reflections_newsletter10
P. 6
REFLECTIONS
Dyslipidaemia
Dyslipidaemia Global Newsletter #10 2025
TREATMENTS AND MODELLING Dyslipidaemia
Global impact of fixed-dose combination therapies on cardiovascular mortality
and events, 2023-2050: A modeling study.
Watkins DA, et al. JACC. 2025 July 14;86(3):149-161.
One of the main challenges in improving CV health is implementing simple, proven interventions among high-risk individuals. Global
data show that the use of front-line therapies (statins, antihypertensives, and antiplatelets) remains low, with only about one in 10
high-risk individuals on a statin. Single-pill combination (SPC) therapies are a promising strategy for both primary and secondary
prevention. However, widespread adoption has been limited by regulatory barriers, slow market entry, and institutional resistance
to new preventive approaches. This study builds on trial evidence to quantify the potential reduction in fatal and non-fatal CVD
outcomes that could be achieved between 2023 and 2050 if SPC therapies were to be adopted worldwide.
The authors used state-transition and demographic modelling to project CV outcomes in 182 countries from 2023 to 2050,
accounting for population growth, aging, and mortality. Six CVD outcomes were modelled: ischemic heart disease, ischemic and
haemorrhagic stroke deaths, non-fatal ACS, stroke, and new-onset heart failure. Two SPC scale-up strategies were compared
against a “current care” reference scenario: a targeted strategy focused on improving adherence and reducing therapeutic inertia in
patients already receiving care, and a population-based approach extending therapy to individuals at intermediate-to-high CVD risk.
The model simulated improvements across the care cascade, awareness, initiation, and adherence, applying pooled SPC trial effects
to reduce CVD incidence and case fatality. Sensitivity analyses examined variations in adoption, adherence, acetylsalicylic acid
(Aspirin) use, and adverse events under the population-based approach.
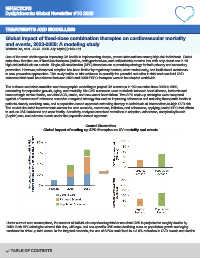
Central illustration
Global impact of scaling up SPC therapies on CV mortality and events
Under current care assumptions, the number of individuals experiencing fatal or non-fatal CVD is projected to roughly double by
2050. Both SPC strategies slowed this rise, with age- and sex-specific CVD rates declining even as population growth and aging
continued to drive up total cases. In the targeted scenario, the use of SPCs could lead to a 3.9% reduction in CVD events and deaths
TABLE OF CONTENTS